In a world characterized by different dietary approaches, we see especially two camps with completely opposing views: plant based diet vs meat based diet.
This decision goes far beyond personal preference and affects not only our health, but also our planet. Let’s take a look at the impact our eating habits have and how we can make conscious choices that support both us and our environment.
The information in today’s article comes from over 2 years of study and the evaluation of numerous studies.
In summary, a plant-based diet is better for our environment and is richer in fiber, antioxidants and some minerals due to the high consumption of vegetables and legumes. However, nutrients such as vitamin B12, iron and omega-3 are rarely found in plant-based foods.
Plant based diet vs meat based diet
Plant-based diet
Plant-based eating is more than just a trend; it’s a way of life that aims to consume mainly plant-based foods.
This does not necessarily mean avoiding meat, but emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes and nuts. The basic principle is to focus on foods that come from nature and are rich in nutrients.
Benefits for your health

Heart health
One of the clear benefits of a plant-based diet is its positive effect on heart health. By eating foods rich in fiber and avoiding saturated fats, the risk of heart disease can be significantly reduced.
Weight management
For those watching their waistline, plant-based diets are a promising option. The fiber-rich composition of plant-based foods promotes a long-lasting feeling of satiety, which in turn can contribute to more effective weight management.
Disease prevention
From diabetes to certain cancers, a plant-based diet is often associated with a lower incidence of disease. The multitude of antioxidants and phytonutrients in plant-based foods boost the immune system and support overall health.
Environmental impact
Reduction of the CO2 footprint
In addition to the personal benefits, a plant-based diet also has a positive impact on our planet. The carbon footprint of a plant-based diet is significantly lower compared to meat production, as plants require fewer resources to grow.
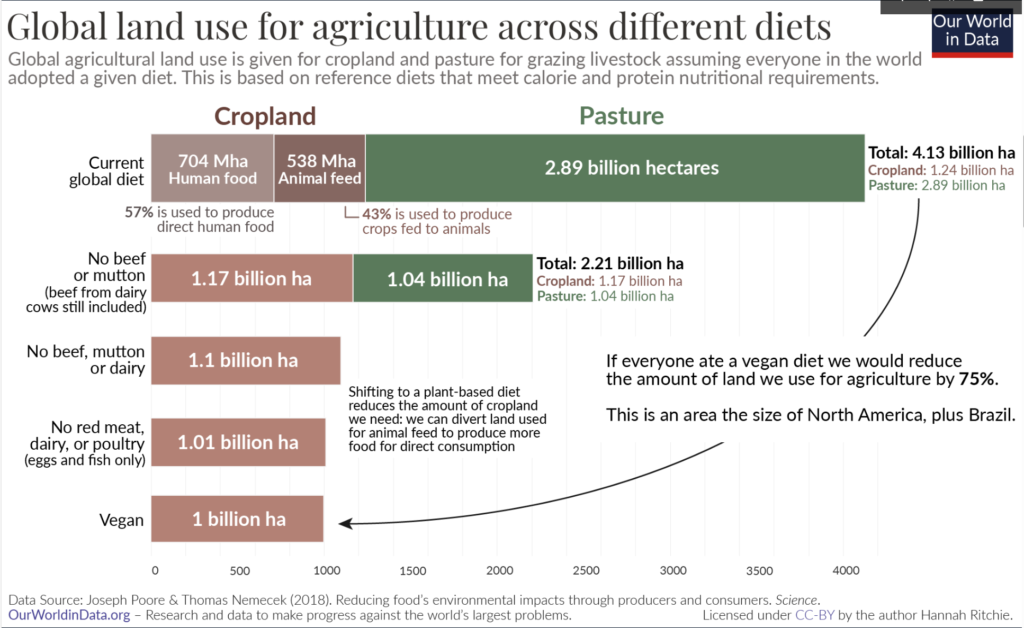
Water foodprint and land use
Growing plant-based food often requires less water and land compared to livestock farming. Switching to a plant-based diet can therefore make an important contribution to the sustainable use of resources and help to preserve the environment.
Meat-based diet
Whether it’s a sausage at a barbecue or a juicy steak at a Sunday family meal, meat has a firm place in many traditional eating habits. Meat-based diets are often linked to cultural and social aspects, making them a significant part of our culinary heritage.

Health effects
Cardiovascular diseases
It is no secret that excessive meat consumption can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. The high saturated fat content in some meats can negatively affect cholesterol levels and lead to heart problems.
Cholesterol and blood pressure
Red meat in particular is often associated with an increase in cholesterol levels. The saturated fats contained in meat can clog the arteries and increase blood pressure, which can lead to serious health problems in the long term.
Cancer risk
Studies suggest that excessive consumption of processed meat may increase the risk of cancer, particularly in relation to bowel cancer. Conservative amounts and high-quality meat sources are therefore crucial to minimize the negative effects.
Environmental impact
Greenhouse gas emissions
Livestock farming, especially cattle, contributes significantly to global greenhouse gas emissions. Methane, which is emitted by ruminants, is a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming.
Land use and deforestation
Intensive land use for livestock farming is a major cause of deforestation. The need for grazing land and fodder cultivation leads to large areas being cleared, which not only endangers biodiversity but also destroys important ecosystems.
Comparison

Nutrient supply
Both plant-based and meat-based diets can provide all the necessary nutrients if they are carefully planned. Nevertheless, there are some nutrients that are particularly critical in the respective form of nutrition
Potential deficiencies in a plant-based diet
- Protein: Plant-based foods often contain less protein compared to animal products. However, it is possible to get enough protein from sources such as legumes, nuts, seeds and soy products. If you want to learn more about protein, you can read this article about macronutrients and there tasks in our body.
- Iron: Plant sources of iron are not absorbed by the body as efficiently as animal sources. To improve absorption, combine your iron sources with foods rich in vitamin c such as lemons or peppers.
- Vitamin B12: This vitamin is mainly found in animal products. People who eat a plant-based diet should take in B12 via fortified foods or food supplements.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Plant sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as flaxseed, walnuts and chia seeds, should be regularly included in a plant-based diet, as these essential fatty acids are often found in fish.
Potential deficiencies in a meat-based diet
- Fiber: Meat does not contain fiber, which is important for digestion. However, a balanced diet should also include fiber-rich plant foods such as whole grains or legumes.
- Antioxidants and phytonutrients: Plant foods are rich in antioxidants and phytonutrients, which are often lacking in a meat-heavy diet.
- Saturated fats: Meat often contains saturated fats, excessive consumption of which can be associated with health problems. Vegetable oils and nuts offer a healthier source of fat.
- Folic acid: Folic acid, important for cell division and blood formation, is found mainly in green leafy vegetables and legumes.
Ethics and animal welfare
The exploitation and killing of living beings can in no way be considered ethical.
Nevertheless, by choosing the right meat, we can at least reduce the suffering caused.
It is certainly debatable whether a plant-based diet in which meat is only eaten twice a week, but from the worst factory farming, is more unethical than a meat-based diet in which the meat is sourced from small regional farms where the animals are provided with sufficient space and hygiene.
Cost factors
The cost of plant-based and meat-based diets can vary greatly. Plant-based foods can be less expensive, but access to high-quality meat can be more expensive. However, long-term health costs should also be considered.
Practical tips for a balanced diet

Flexitarianism
For those who don’t want to completely commit to one side, flexitarianism offers a balanced option. You can reduce meat consumption without eliminating it completely. This allows for a more flexible and sustainable diet.
Meal planning
Good meal planning is crucial, regardless of the diet you choose. Make sure your meals are balanced and contain all the necessary nutrients. Experiment with different plant-based proteins and meat alternatives.
Quality-conscious meat consumption
When choosing meat, be quality conscious. Buy meat from trusted sources that support sustainable and ethical practices. Reduce portions and choose lean meats to minimize negative health effects.
Always chose biological meat and aninmal-products if possible. Not only to minimize suffering but to minimize the antibiotic residues it contains
Conclusion
There is no universal “right” answer in the plant-based vs. meat-based diet debate. It comes down to personal preferences, ethical considerations and individual health goals.
By consciously choosing a balanced diet, we can not only promote our own health, but also actively contribute to the sustainable development of our planet.
You have the power to make positive changes through your eating habits – be it with a juicy veggie burger or a delicious piece of sustainable meat.
What are the advantages of a plant-based diet compared to a meat-based diet?
A plant-based diet contains more antioxidants, fiber and folic acid due to the large amount of vegetables.
Which nutrients can be critical in a plant-based diet?
Especially the long-chain omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, vitamin B12 and iron are rarely found in plant-based foods.
How does a plant-based diet affect the environment compared to a meat-based diet?
Plant-based foods generally use up less CO2, water and land than meat and are therefore better for the environment.
How can you meet your protein requirements in a plant-based diet?
Whole grains, pulses, nuts and seeds as well as products such as tofu and tempeh are high-quality plant-based sources of protein.
If you liked this post about “plant based diet vs meat based diet”, you might also enjoy this article explaining the basic principles about a healthy diet.
In addition, I would really appreciate it, if you leave your personal opinion about plant based or meat based diets in the comments.
Thank you and see you soon.







